Selection at silent sites in the human genome
The genomes of warm-blooded vertebrates appear to be organized into mosaic patterns of long stretches (>300 kb) of compositionally homogeneous "isochores". The G+C content of isochores varies from 30 to 60%, and the base composition of coding regions, introns, and flanking regions of a given gene is strongly correlated with that of the isochore in which it resides. Such patterns have complicated the study of translational constraints at silent sites. We took advantage of alternatively spliced genes to perform within-gene tests of translational selection; among codons in an alternatively spliced gene, those in constitutively expressed exons are translated more often than those in alternatively spliced exons. Thus, translational selection should act more strongly to bias codon usage and reduce silent divergence in constitutive than in alternatively spliced exons. By controlling for regional forces affecting base-composition evolution, this within-gene comparison makes it possible to detect codon selection at synonymous sites in mammals. We found that GC-ending codons are more abundant in constitutive than alternatively spliced exons in both Drosophila and humans. Contrary to our expectation, however, silent DNA divergence between mammalian species is higher in constitutive exons than in alternatively spliced exons. The interpretation of this result is complicated by CpG islands and changes in base composition between species. Although our study provides some support for codon selection in humans, our understanding of translational selection in mammals remains less clear than in E. coli, yeast, and Drosophila.
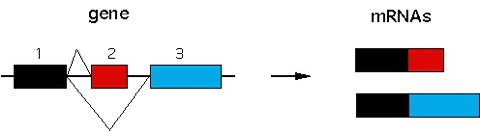
Figure 1. Alternative splicing to create mature mRNA.
Exons 1 and 2 and exons 1 and 3 are spliced to form two isoforms of the gene depicted.In such alternatively spliced genes, constitutively expressed exons (exon 1 in the figure) are expressed at higher levels that alternatively spliced exons (exon 2 and 3 in the figure).
References
- A test of translational selection at “silent” sites in the human genome: base composition comparisons in alternatively spliced genes.
- Gene 261:93–105. 2000.